 |
 |
- Search
| Korean J Helicobacter Up Gastrointest Res > Volume 20(1); 2020 > Article |
|
Abstract
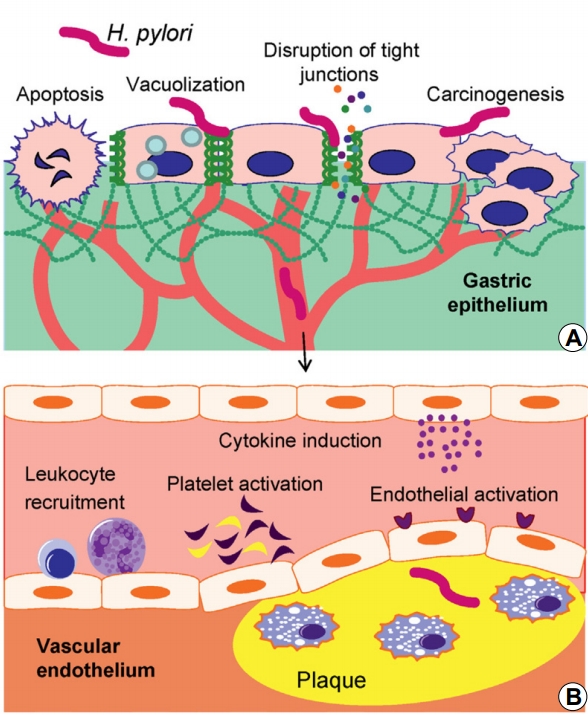
Fig.Ā 1.
TableĀ 1.
| Reference | Study design | Objects | Test for HP | Results | Other remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mendall et al. [1] (UK, 1994) | Single center, case-control | 111 CHD, 74 controls | HP IgG (ELISA) | Associated OR 2.15 (1.07~4.29) | |
| Murray et al. [2] (UK, 1995) | Cross-sectional | 1,182 men, 1,198 women | HP IgG (ELISA) | Not associated OR 1.51 (0.93~2.45) | |
| Folsom et al. [3] (USA, 1998) | Prospective, case-cohort (F/U 3.3 years) | 498 cohort, 217 CHD | HP IgG (ELISA) | Not associated OR 1.03 (0.68~1.57) | |
| Pasceri et al. [4] (Italy, 1998) | Single center, case-control | 88 IHD on the angiography, 88 age-sex matched controls | HP IgG (ELISA) | Associated OR 2.8 (1.3~7.4) | āCAD risk in CagA (+) OR 3.8 (1.6~9.1) |
| CagA IgG (Western blot) | |||||
| Danesh [5] (UK, 1999) | Case-control | 1,122 AMI, 1,122 age-sex matched controls | HP IgG (ELISA) | Associated OR 1.75 (1.29~2.36) | |
| Pellicano et al. [6] (France, 1999) | Meta-analysis of 24 studies | 6,603 sample size | HP IgG (ELISA) or UBT | Possible weak association Pooled OR 1.55 (1.38~1.74) | |
| Whincup et al. [7] (UK, 2000) | Multicenter, prospective, nested case-control (F/U 9.5 years) | 505 CHD, 1,026 controls | HP IgG (ELISA) | Not associated OR 1.3 (0.88~1.90) | Not āCAD risk in CagA (+) OR 1.1 (0.17~1.71) |
| CagA IgG (ELISA) | |||||
| Zhu et al. [8] (USA, 2002) | Study 1: cross-sectional | Study 1: 391 angiography ā 63% CAD | HP IgG (ELISA) | Not associated | |
| Study 2: single center, prospective longitudinal (F/U 3 years) | Study 2: 929 CAD on angiography | āStudy 1: OR 1.03 (0.60~1.77) | |||
| āStudy 2: HR adjusted for HP IgG (+) 1.12 (0.81~1.54) | |||||
| Kinjo et al. [9] (Japan, 2002) | Multicenter, prospective, case-control | 618 AMI, 967 controls | HP IgG (ELISA) | Associated in subgroup <55 years OR 0.97 (0.71~1.32) | Subgroup <55 years OR 2.97 (1.37~6.41) |
| Fraser et al. [10] (New Zealand, 2003) | Case-control | 341 AMI, 831 controls | HP IgG (ELISA) | Associated OR 1.34 (1.00~1.80) (P=0.038) | |
| Sheehan et al. [11] (Ireland, 2005) | Case-control | 227 ACS, 227 age-sex matched controls | HP IgG (ELISA) | Not associated OR 0.9 (0.8~1.0) | |
| Jin et al. [12] (Korea, 2007) | Single center, prospective, case-control | 175 CAD on angiography, 88 controls with normal angiography | Histology | Not associated | |
| āNo difference in HP infection rate between CAD and controls (40.6% vs. 30.7%) | |||||
| Zhang et al. [13] (China, 2008) | Meta-analysis of 15 case-control studies | 2,157 CHD, 2,283 controls | CagA IgG (ELISA or Western blot) | CagA infection is associated with susceptibility to CHD OR (random) 2.11 (1.70~2.62) | |
| Tamer et al. [14] (Turkey, 2009) | Single center, case-control | 152 CAD (73 ACS, 79 SA), 22 controls | HP IgG (ELISA) | Associated āprevalence of HP IgG in CAD (80.2% vs. 54.4%, P=0.015) | No difference in HP IgG (+) rate between ACS and SA |
| Khodaii et al. [15] (Iran, 2011) | Single center, case-control | 500 AMI on angiography, 500 controls | HP IgG (ELISA) | Associated OR (crude) 2.57 (1.89~3.49) | AMI risk in CagA (+) OR (crude) 1.67 (1.18~2.36) |
| CagA IgG (ELISA and Western blot) | |||||
| Schƶttker et al. [16] (Germany, 2012) | Population-based cohort (F/U 5.1 years) | 9,953 participants ā 170 AMI (+) | HP IgG (ELISA) | Not associated OR 0.7 (0.46~1.08) | CagA (+) HR 1.09 (0.76~1.57) |
| CagA IgG (ELISA) | |||||
| Lai et al. [17] (Taiwan, 2015) | Nationwide retrospective cohort (Taiwan National Health Insurance Research Database) | 17,075 HP infected cases, 68,300 age-sex matched controls | ICD-9-CM (HP infection and ACS) | Associated HR 1.48 (1.30~1.69) | |
| Yu et al. [18] (China, 2017) | Meta-analysis of 26 cross-sectional studies | 3,901 CAD, 2,751 controls | HP IgG (ELISA) | Associated OR 1.42 (1.09~1.86) | Younger individuals OR 2.36 (1.50~3.73) |
| Histology | |||||
| Stool antigen | |||||
| Rahmani et al. [19] (Iran, 2017) | Meta-analysis of 11 case-control studies | 1,253 AMI, 1,264 controls | HP IgG (ELISA) | Associated OR 2.53 (1.37~4.67) | |
| Lee et al. [20] (Korea, 2018) | Cross-sectional | 463 subjects who underwent CLO, PWV, and MDCT (239 CLO negative, 224 CLO positive) | CLOtest | Associated CLO positive group more likely to have significant coronary artery stenosis OR 2.81 (1.05~7.52) | |
| Wang et al. [21] (Taiwan, 2018) | Nationwide retrospective cohort (Taiwan National Health Insurance Research Database) | 3,713 HP eradication within 365 days group, 55,249 HP non-eradication group, propensity score matching | ICD-9-CM | Associated Decreased association of CHD in eradication group (2.58% vs. 3.35%) Mortality rate was lower in eradication group (2.86% vs. 4.43%) |
HP, Helicobacter pylori; CHD, coronary heart disease; IgG, immunoglobulin G; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; OR, odds ratio; F/U, follow-up; IHD, ischemic heart disease; CagA, cytotoxin-associated gene A; CAD, coronary artery disease; AMI, acute myocardial infarction; UBT, urea breath test; HR, hazard ratio; ACS, acute coronary syndrome; SA, stable angina; ICD-9-CM, International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification; CLO, campylobacter like organism; PWV, pulse-wave velocity; MDCT, multidetector computed tomography.
Adapted from the book of Lim. Extraintestinal manifestations of H. pylori infection: heart disease. 2016:349-360, with permission from Springer Singapore. [22]
TableĀ 2.
| References | Study design | Subjects | Test for HP | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Montenero et al. [48] (Italy, 2005) | Single center, case-control | 59 AF 45 controls | HP IgG (ELISA) | HP seropositivity in AF is higher than that in controls (97.2 IU/mL vs. 5.3 IU/mL, P<0.001) |
| Badran and Mahfouz [49] (Egypt, 2007) | Single center, case-control | 82 AF 80 controls | HP IgG (ELISA) | CagA strain showed a higher prevalence in the AF group |
| CagA IgG (ELISA) | ||||
| Platonov et al. [50] (Sweden, 2008) | Single center, case-control | 72 AF 72 controls | HP IgG (EIA) | No difference in HP seropositivity between AF and controls (57 % vs. 55 %, ns) |
| Bunch et al. [51] (USA, 2008) | Single center, case-control | 83 AF 660 controls | HP IgG (ELISA) | HP seropositivity in AF is higher than that in controls (65 % vs. 55 %, P=0.049) |
| Lunetta et al. [52] (Italy, 2009) | Prospective, follow-up 7 years | 120 HP (+) 60 HP (-) | HP IgG | No difference in development of AF between HP (+) vs. HP (-) (21% vs. 18%, ns) |
| Ki et al. [53] (Korea, 2010) | Single center, case-control | 60 AF 36 controls | HP IgG (ELISA) | The levels of anti-VacA antibodies were significantly higher in AF |
| VagA IgG (ELISA) | ||||
| Franceschi et al. [54] (Italy, 2013) | Single center, case-control | 54 dysrhymia 50 controls | UBT | No difference in HP IgG (+) between pts vs. controls (42 % vs. 44 %, ns) |
| CagA IgG (Western blot) | ||||
| Wang et al. [55] (China, 2015) | Single center, case-control | 285 AF 300 controls | HP IgG (ELISA) | The values of Hp in patients with long-standing AF were significantly higher than those in short-standing AF and control groups |
HP, Helicobacter pylori; AF, atrial fibrillation; IgG, immunoglobulin G; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; IU, international unit; CagA, cytotoxin-associated gene A; EIA, enzyme immunoassay; ns, not significant; VagA, vacuolating cytotoxin; UBT, urea breath test.
Adapted from the book of Lim. Extraintestinal manifestations of H. pylori infection: heart disease. 2016:349-360, with permission from Springer Singapore. [22]
REFERENCES
-
METRICS

-
- 1 Crossref
- 4,328 View
- 179 Download
- Related articles in Korean J Helicobacter Up Gastrointest Res
-
Can Helicobacter pylori Infection Reduce the Efficacy of Cancer Immunotherapy?2023 December;23(4)
Role of Helicobacter pylori Eradication Therapy in Patients with Functional Dyspepsia2023 June;23(2)
Helicobacter pylori Infection and the Risk of Osteoporosis in Women2022 March;22(1)
How Does a Helicobacter pylori-infected Spouse Affect an Uninfected Spouse?2021 December;21(4)
Benefits of Helicobacter pylori Eradication on Extragastric Diseases2021 December;21(4)