위 상부 체부의 국소적인 거대주름
A Focal Giant Fold in the Upper Gastric Body
Article information
요약: 61세 남자가 상복부 통증으로 시행한 위내시경 검사에서 위의 거대주름이 보여 병원에 왔다. 최근 6개월간 8 kg의 체중 감소가 있었으며, 약물 복용력이나 타질환의 병력은 없었다. 위내시경 검사 시 상부 체부 대만-후벽측에 국소적인 거대주름이 관찰되었으며(Fig. 1A), 공기를 주입 시 위는 잘 팽창되었지만 거대 주름의 형태와 크기는 차이가 없었다. 생검 겸자로 주름을 눌렀을 때 주름의 윗부분은 비교적 부드러웠지만, 좀 더 깊은 부위는 딱딱하였다(Fig. 1B). 협대역내시경(narrow-band imaging) 시행 시 위소구(area gastricae)의 확장 소견이 관찰되었으며(Fig. 1C), 확대내시경(magnifying endoscopy)을 사용하여 확대 관찰 시 위점막의 표면미세구조 및 미소혈관의 불규칙성은 관찰되지 않았다(Fig. 1D). 내시경 초음파 검사(EUS)에서는 거대주름은 주로 점막하층과 고유근층의 두꺼워짐으로 인한 소견이었으며, 이는 위 바깥쪽의 저에코 병변과 연결되어 있었다(Fig. 2). Helicobacter pylori에 대한 신속요소 분해효소 검사는 음성이었다.

Endoscopic findings. (A) A focal giant fold is seen on the greater curvature-posterior wall of the upper gastric body. (B) On compressing with biopsy forceps, the superficial portion of the giant fold feels soft; however, its deep portion feels somewhat hard. (C) On narrow-band imaging (NBI), prominent areae gastricae are clearly visible. (D) Magnifying endoscopy with NBI reveals regular microsurface and microvascular patterns.
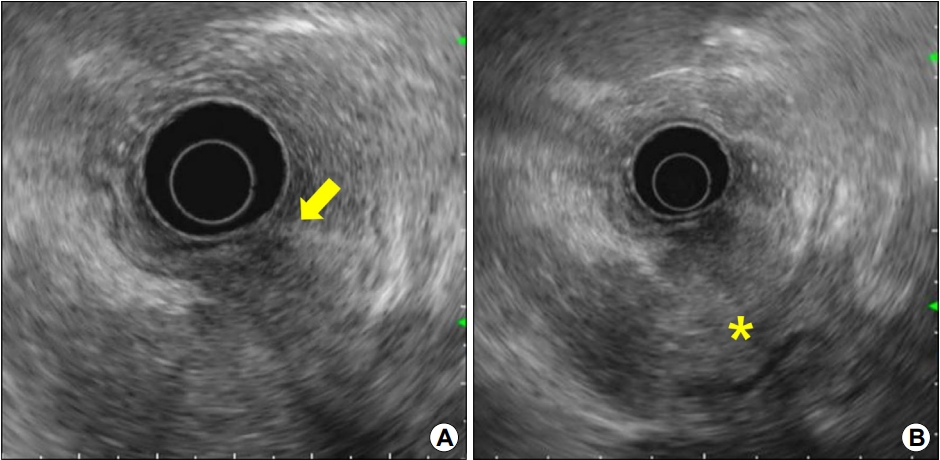
Endosonographic findings. (A, B) The giant fold is primarily caused by the thickening of the submucosa and muscularis propria (arrow), which are connected to a large, irregular hypoechoic lesion located outside the stomach (asterisk).
상기 환자에서 거대주름의 원인으로 가능성이 높은 질환은?
해설: EUS 소견을 토대로 상부 체부의 거대주름은 위벽 바깥의 저에코 병변에 의한 이차적인 변화로 판단되었으며, 저에코 병변은 주로 췌장의 미부에 위치하고 있었다. 췌장암을 의심하여 복부 전산화단층촬영 검사를 시행하였으며, EUS 소견과 동일하게 췌장 미부에 7 cm 크기의 저음영 종괴가 위체부를 침윤하고 있었다(Fig. 3). 췌장 미부 병변에 대해 EUS 유도하 세포흡인 검사(EUS-guided fine-needle aspiration, EUS-FNA)를 시행하였으며, 최종적으로 췌장 샘암종으로 진단되었다(Fig. 4).
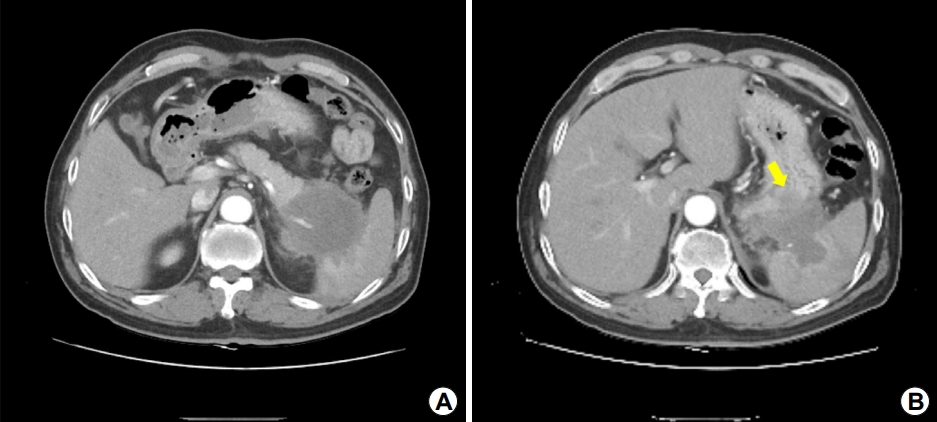
Abdominal computed tomography findings. (A) An irregular hypodense mass, approximately 7 cm in size, is seen in the pancreatic tail; the mass invades the spleen. (B) Furthermore, the mass invades the posterior wall of the upper gastric body (arrow).
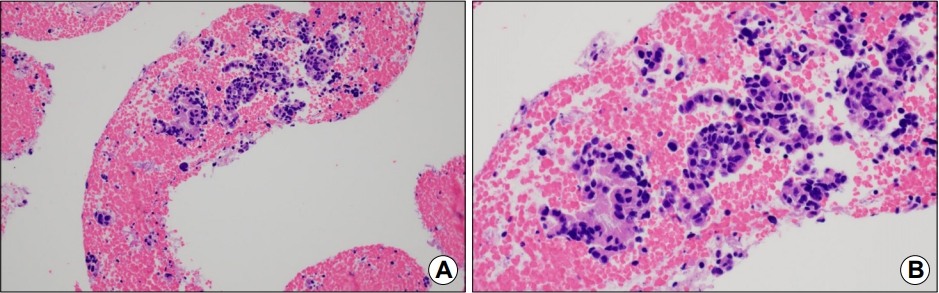
Histopathologic findings. (A) Atypical epithelial cells with a high nuclear/cellular ratio are seen exhibiting aggregation and fusion (H&E stain, ×100). (B) These cells form a glandular structure (H&E stain, ×400).
정상 위에서는 근층의 면적보다 점막층과 점막하층의 면적이 넓기 때문에 위에 주름이 생기게 된다. 정상 위 점막주름의 평균 높이와 넓이는 각각 7 mm, 3 mm이며, 위의 거대주름은 내시경 검사 시 충분한 공기를 주입하더라도 점막주름이 10 mm 이상으로 두꺼워져 있는 경우를 일컫는다. 내시경 검사 시 이러한 위의 거대주름이 발견될 시에는 주름이 국소성인지 미만성인지를 평가하고, 또한 주름을 구성하는 병변이 위벽 내 어느 층에 위치하는가를 알아내는 것이 중요하다. 점막층에 주병변이 있는 경우에는 위벽의 신축성이 비교적 잘 유지되고 공기 주입의 정도에 따라 주름의 직경이 감소하는 소견을 보인다. 반면 점막하층이나 고유근층의 요소가 많아질수록 위벽의 신축성이 감소되고 주름이 울퉁불퉁하고 딱딱한 외관을 보이며 주름과 주름 사이의 골이 벌어지지 않게 된다. 또한 거대주름 위의 위소구 구조를 확대내시경으로 관찰하는 것도 중요한데, 점막층에 부종성 변화가 있는 경우에는 위소구가 발적성 변화를 동반하며 암침윤이 있는 경우에는 위소구의 불규칙성이 관찰된다[1]. 반면 본 증례와 같이 위벽 바깥쪽에서 침윤하는 경우는 점막구조는 비교적 정상적으로 유지되는 경우가 많다.
거대주름의 진단을 위해 조직 검사를 고려할 수 있지만, 일반적인 생검 겸자에 의한 조직 검사로는 점막 표면의 일부만 생검이 가능하므로 심부 점막층이나 점막하층, 고유근층에 병변이 있는 경우에는 진단에 제한점이 있다. 따라서 직경이 큰 생검겸자를 사용하거나 내시경적 박리생검법(strip biopsy), 상황에 따라서는 EUS-FNA를 시행하기도 한다. 또한 Borrmann 4형이 강력히 의심될 시에는 조직 검사의 확진이 어려운 경우 바로 위절제술을 시행하는 경우도 있다.
EUS는 상부위장관의 악성 병변의 진단과 병기 평가에 흔히 사용되고 있으며, 특히 위장관 벽의 층구조를 보는데 있어서는 전산화단층촬영 검사에 비해 정확도가 우월하다. 거대주름의 경우에는 병소가 점막층, 점막하층, 고유근층 중 어느 부위에 위치하는가를 확인하는 데 매우 유용하며, 본 증례와 같이 위 주위 장기 병변과의 연관성을 파악하는 데에도 큰 도움이 된다[2]. 일반적으로 거대주름의 병소가 주로 점막층에 있는 경우는 양성 병변일 가능성이 많으며, 병소가 점막하층이나 고유근층, 특히 본 증례와 같이 주위 장기 병변과 연결되어 있을 시에는 악성 병변의 가능성이 많다[3]. 하지만 급성 췌장염으로 인해 염증이 위체부로 파급된 경우에도 본 증례와 같은 부위에 거대주름이 발생할 수 있으므로, 급성 복통과 같은 증상과 단기간 내 거대주름 형태나 크기의 변화도 거대주름의 감별 진단에 유용하다.
본 증례를 고찰해보면 거대주름이 상부 체부 대만-후벽측에 국한되어 있었다는 점, 공기 주입 시에도 비교적 거대주름의 형태가 변하지 않고 겸자로 눌렀을 때 심부 부위가 딱딱하였다는 점으로 보아 거대주름의 원인이 악성 병변임을 의심할 수 있고, 확대 관찰 시 위점막의 표면 미세구조 및 미소혈관의 불규칙성이 없었다는 점으로 점막 병변보다는 점막하층 및 고유근층에 악성 병변이 침윤했을 가능성을 많음을 시사한다. 따라서 위 주위의 해부학적 구조를 고려해보면 췌장 미부의 악성 병변이 위 침윤 시에는 본 증례와 같은 거대주름을 유발할 수 있음을 유의하여야 할 것이다.
Notes
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
